Reliability Analysis
Reliability Analysis has become indispensable for modern plant operations as it can ensure that maintenance and life cycle costs are minimized, and availability and uptime are maximized. A number of activities are very useful in ensuring that highly reliable solutions are engineered when required, equipment problems are detected and prevented before they escalate, failures are investigated in a manner that prevents repeat problems, and importantly the cost of spare parts and their storage is minimized. These activities include RAM RCM and RCA.
Advanced Analysis offers solutions in partnership with Reliasoft.

Watch this short video on how PDF2RBD can automate your reliability process
PFD2RBD
PFD2RBD (Read as 'PFD to RBD') is a revolution in RAM Analysis.
The software is a much needed development for large projects with hundreds of thousands of assets. PFD2RBD automates the expensive, time consuming and tedious task of creating RBDs and cuts the cost of this process to a fraction of its manual cost.
The larger the job the more the savings and, of course, once the library is setup, then the issue of errors and inaccuracies inherent in the manual process disappears.
The software will read in a *.pdf of any drawing, PFD, P&ID or anything else. It searches for library items in each drawing, and once it identifies an item, it will add it to a list and allow you to enter any data associated with RAM analysis finally outputting an *.xml file which can be imported into Reliasoft’s Blocksim ready for analysis.
RCM Analysis
Reliability-Centered Maintenance (RCM), is an industrial improvement approach focused on identifying or establishing the operational, maintenance, and capital improvement policies that will manage the risks of equipment failure most effectively. The key technical standards for this activity are SAE JA1011 as well as SAE JA 1012.
RCM allows us to characterize a maintenance program and also allows us to identify the most cost-effective task for all potential failure modes based on actual data. Its implementation can mean significant reduction in downtime and lower costs of operation and maintenance.
The RCM analysis is performed roughly in the following procedure:
1- Gather equipment failure history data and associated costs for Quantitative RCM and import into the RCM Software. We typically use RCM++ other software can also be used.
2- Select a few assets to start with - you can carry out RCM for the highest risk items, the assets with the highest criticality or the very badly behaved (problem actors) and perform FMEA.
3- For each Failure Mode, document the current Maintenance Strategies and Tasks as well as the associated data.
4- Review the current Maintenance Strategies and Tasks, and revise based on the criticality of the failure mode (e.g. introduce a new strategy for high or medium criticality failures).
RCM is a Live Document and should continuously be reviewed and revised, accordingly.
RAM Analysis
Monte Carlo simulation is a useful technique used in various analyses.
An interesting application of Monte Carlo in analyzing upper atmosphere flows can be found here:
https://ntrs.nasa.gov/archive/nasa/casi.ntrs.nasa.gov/20040085340.pdf
Monte Carlo simulation involves the repeated use of random values to simulate a more complex system.
In the case of RAM analysis of systems, the simulation process uses a reliability-wise representation of the system and its components. Data collected from the actual system and its components are used to determine the inputs to this model. Wherever applicable, probabilistic models are used to define these inputs. A random number generator is then used to generate random values based on these distributions. The random values are used to predict the behavior of the system based on the specified system reliability configuration.
The process is repeated a large number of times and system behavior data from each run are recorded. The recorded data are processed using statistical techniques to obtain various results pertaining to the system behavior. These results or outputs are studied and used to make decisions to improve the performance of the system.
The simulation used in reliability engineering is discrete event simulation. In discrete event simulation, the system behavior is represented as a sequence of events. An event occurs at a particular instant and changes the state of the system. The simulation then jumps to the next event.
In reliability engineering, the events are failures, repairs and maintenance actions. The system states are system up (operating) or down (not operating).
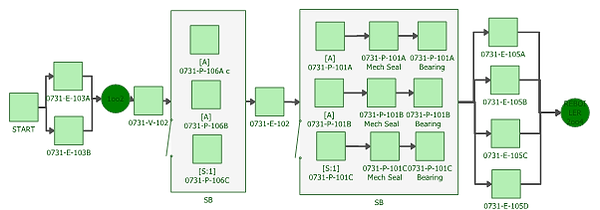
A reliability block diagram in Reliasoft's BLOCKSIM
RCA Analysis
For Root Cause Analysis (RCA), we use Failure Reporting, Analysis and Corrective Action System (FRACAS), which is also used in safety/risk minimization systems and process control systems, root cause analysis and incident reporting systems.
The fundamental tasks of the process include recording failures and associated information and prioritizing them, as well as, identifying, implementing and verifying corrective actions. This information allows for the support of reliability data analysis.
Summaries of incidents counts, and data used for reliability and quality metrics is then easily output from the process. One (of several) software packages we use for this process is Reliasoft's XFRACAS.

Reliasoft's XFRACAS workflow
